Synthetic Materials for Industrial Floorings
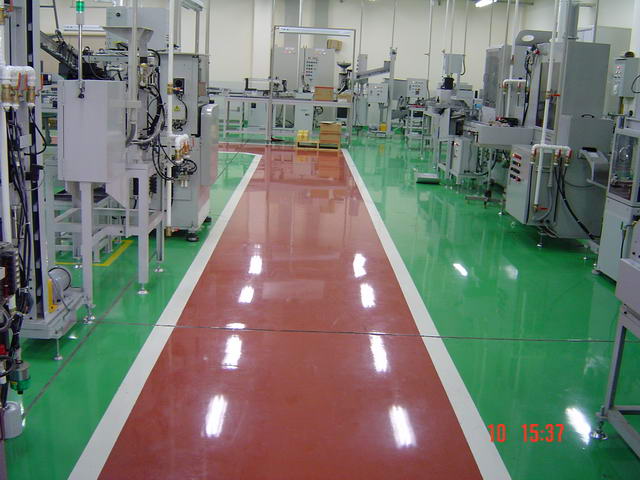 Chemical composition of synthetic materials for industrial flooring includes: Filler, Pigments, Additives, Solvents and/or water.
Chemical composition of synthetic materials for industrial flooring includes: Filler, Pigments, Additives, Solvents and/or water.
Binder
- Macromolecular organic connection. Macromolecules are molecules with a molar mass from 10.000 g/mol upwards, up to several million g/mol. A macromolecule or a collective of macromolecules, which are formed via a Polyreaction are called Polymer. Polymers develop due to the linkage of hundreds of basic molecules (“monomers”) to form large molecules
- Defines the polymer structure.
- Dictates the basic technical properties, such as mechanical and chemical resistance etc.
Filler
- Inorganic solids (chalk, quartz flower etc.) or solid organic polymers
- Influences the mechanical properties, such as flow, surface structure etc.
Pigments
- Inorganic and/or organic solids with “chromophoric” properties (carbon black, oxides /phthalocyanine)
- Define the specific colour shades
Additive
- Usually low molecular organic connection
- Control specific material properties, such as aesthetics, de-earation, adhesion etc.
Solvents
- Inert, usually synthetic organic fluids
- Influence the flow properties, curing times etc.
Water
- Dispersion